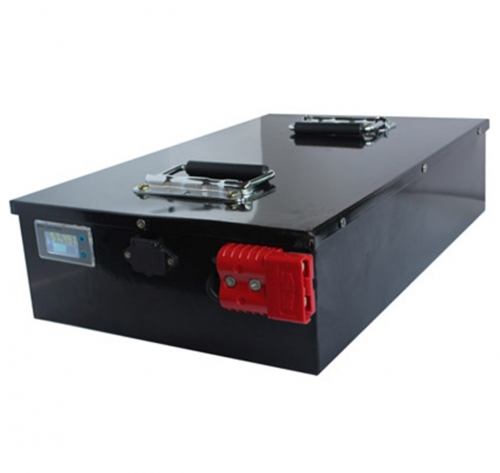
What are the main types of custom lithium batteries? According to the different electrolyte materials used in custom lithium batteries, custom lithium batteries are divided into liquid lithium-ion batteries and polymer lithium-ion batteries.
Rechargeable lithium batteries are widely used in modern digital products such as mobile phones and laptops, but they are relatively "delicate" and cannot be overcharged or over-discharged during use (which will damage the battery or make it scrapped). Therefore, there are protective components or protection circuits on the battery to prevent expensive battery damage. Lithium-ion battery charging requires very high requirements. To ensure that the termination voltage accuracy is within ±1%, major semiconductor device manufacturers have developed a variety of lithium-ion battery charging ICs to ensure stable, reliable and fast charging.
Mobile phones basically use customized lithium batteries. Correct use of lithium-ion batteries is very important to extend battery life. It can be made into flat rectangular, cylindrical, rectangular and button-shaped according to the requirements of different electronic products, and there are battery packs composed of several batteries connected in series and parallel. The rated voltage of lithium-ion batteries is generally 3.7V due to material changes, and the positive electrode of lithium iron phosphate (hereinafter referred to as ferrophosphorus) is 3.2V. The termination charging voltage when fully charged is generally 4.2V, and ferrophosphorus 3.65V. The termination discharge voltage of lithium-ion batteries is 2.75V to 3.0V (battery manufacturers give the operating voltage range or the termination discharge voltage, and the parameters are slightly different. Generally, it is 3.0V, and 2.5V for ferrophosphorus). Continuing to discharge below 2.5V (2.0V for ferrophosphorus) is called over-discharge, which will damage the battery.
Lithium-ion batteries with lithium cobalt oxide type materials as positive electrodes are not suitable for large current discharge. Excessive current discharge will reduce the discharge time (higher temperature will be generated inside and energy will be lost), and may be dangerous; but lithium iron phosphate positive electrode materials lithium batteries can be charged and discharged at a large current of 20C or even higher, which is particularly suitable for electric vehicles. Therefore, the discharge current given by the battery manufacturer should be less than the discharge current during use. Lithium-ion batteries have certain temperature requirements. The factory provides the charging temperature range, discharge temperature range and storage temperature range. Overvoltage charging will damage lithium-ion batteries. The charging current of lithium-ion batteries should be based on the recommendations of the battery manufacturer, and a current limiting circuit is required to avoid overcurrent (overheating). The commonly used charging rate is 0.25C~1C. When charging with high current, the battery temperature is often detected to prevent overheating and damage to the battery or explosion.
Customized lithium batteryCharging is divided into two stages: constant current charging first, and then changing to constant voltage charging when it is close to the termination voltage. For example, a battery with a capacity of 800mAh has a termination charging voltage of 4.2V. The battery is charged at a constant current of 800mA (charging rate of 1C). At the beginning, the battery voltage increases at a large slope. When the battery voltage approaches 4.2V, it is changed to 4.2V constant voltage charging. The current gradually decreases and the voltage does not change much. When the charging current drops to 1/10-50C (the setting value varies from factory to factory and does not affect the use), it is considered to be close to full charge and charging can be terminated (some chargers start the timer after reaching 1/10C and end charging after a certain period of time).